SIRIM 55 ESG Certification. A Practical Guide for Malaysian Companies
- 24/08/2025
- Posted by: Ildar Usmanov
- Categories: Compliance, Regulations

Introduction: What is SIRIM 55 ESG Certification?
Malaysia has introduced the SIRIM 55 ESG Certification (SIRIM 55:2023 ESG Management System standard), for which SIRIM QAS offers certification. Unlike voluntary statements, this standard sets out structured requirements for leadership, planning, and continuous improvement.
This article explains the core clauses of SIRIM 55:2023, how it works in practice, and what companies need to prepare before seeking certification. We will also explore the regulatory context, the challenges firms face, and the benefits of building an ESG management system.
Whether you are an SME starting from zero, or a PLC preparing for investor scrutiny, this guide will help you understand why ESG management system SIRIM 55 matters and how to get ready.
Why SIRIM 55 ESG Certification Matters
Global and local expectations are converging. Investors, regulators, and supply chains demand proof that companies manage ESG risks and opportunities in a structured way. Reports alone are no longer enough—auditable systems are required.
The SIRIM 55 ESG Certification addresses this need. By certifying that an organisation has an ESG management system in place, companies can:
- Build trust with investors and lenders seeking credible ESG performance.
- Reduce the risk of greenwashing by aligning with national and international frameworks.
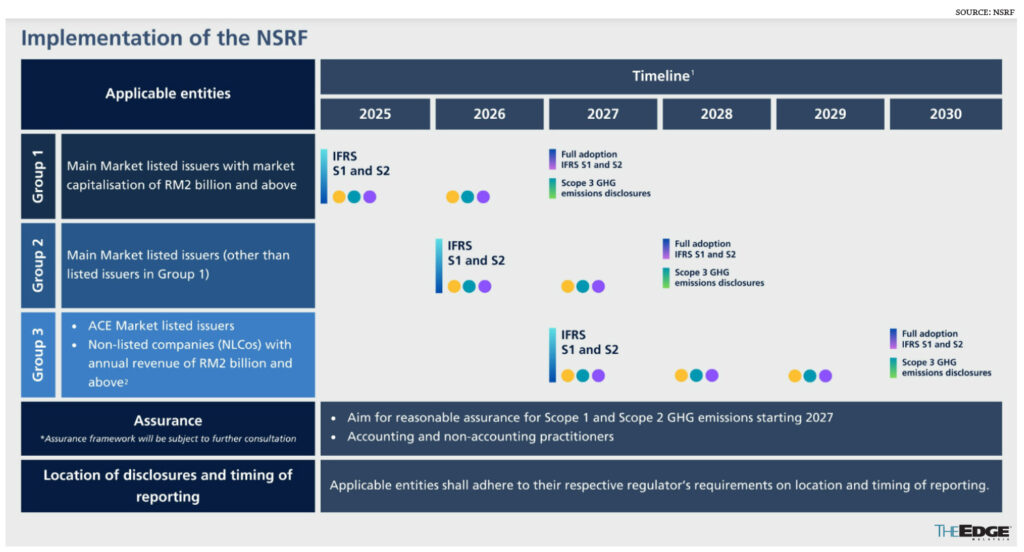
- Prepare for evolving disclosure rules as Bursa Malaysia has already announced phased adoption of the IFRS S1 and S2 standards, starting with PLCs and large non-PLC companies.
- Improve operational resilience through systematic risk and performance tracking.
Poor disclosure can lead to reputational damage, missed financing opportunities, and compliance risks. Strong ESG governance, in contrast, creates value, improves supply-chain positioning, and enhances long-term competitiveness.
Regulatory Landscape: Malaysia and Global
Malaysia’s ESG ecosystem is expanding quickly:
- Bursa Malaysia requires listed issuers to publish sustainability reports aligned with global standards.
- SIRIM 55:2023 introduces an auditable ESG management system standard.
- SIRIM 56:2024 is a reporting standard. It sets out how companies should disclose ESG information and includes requirements for independent verification of reports. Unlike SIRIM 55, it is not a certification scheme, but SIRIM QAS provides verification services based on it.
- The government’s National Industry ESG (i-ESG) Framework sets out Phase 1 (2024–2026) for capacity building and Phase 2 (2027–2030) to accelerate compliance.
Globally, multiple frameworks interlink with Malaysia’s approach:
- GRI Standards set global benchmarks for sustainability disclosures.
- IFRS S1 & S2 (ISSB standards) focus on financially material ESG and climate risk disclosures.
- SASB Standards provide sector-specific KPIs for investors.
- TCFD and SBTi address climate risk and decarbonisation pathways.
SIRIM 55 ESG Certification serves as a bridge: it creates a management system that supports compliance with Bursa Malaysia requirements, aligns with GRI, and provides the governance backbone for IFRS and SASB disclosures.
This makes it especially relevant for PLCs and supply-chain exposed companies facing global buyer requirements.
Key Challenges Companies Face in SIRIM 55 ESG Certification
Implementing SIRIM 55 ESG Certification is not without challenges:
- Data quality and availability – many companies lack reliable ESG metrics.
- Overlapping frameworks – confusion between GRI, IFRS, SASB, Bursa, and now SIRIM 55.
- Internal expertise – few firms have trained ESG managers or auditors.
- Stakeholder engagement – insufficient consultation leads to weak materiality assessments.
- Assurance complexity – preparing for external audits requires structured evidence and governance.
SMEs often face resource constraints, while larger companies struggle with data integration across departments. Without external support, certification readiness can become a costly, time-consuming process.
How SIRIM 55 Works: Clause-Level Breakdown
The SIRIM 55:2023 ESG Management System is structured around five main clauses:
- Context of the Organisation – Define organisational boundaries, ESG risks, and stakeholder expectations.
- Leadership – Establish governance, ESG policies, and assign top management accountability.
- Operation – Implement processes, allocate resources, and engage stakeholders in ESG activities.
- Support – Provide training, communication, resources, and documented information to sustain the system.
- Improvement – Review performance, address non-conformities, and continually enhance ESG practices.
This ensures ESG is integrated into the organisation’s ongoing processes, not treated as a separate silo.
Audit expectations: Certification involves a two-stage audit by SIRIM QAS or an accredited body. Stage 1 checks documentation and readiness. Stage 2 verifies implementation and effectiveness. Surveillance audits follow annually. This follows the same model as other SIRIM management system certifications
This structure ensures that ESG becomes part of core business operations, not just an annual reporting exercise.
Best Practices & Tips
To succeed with SIRIM 55 ESG Certification, companies should:
- Start early – allow at least 6–9 months for full readiness.
- Align ESG with strategy – integrate into core business goals, not as a separate function.
- Engage stakeholders – consult employees, suppliers, and customers to define material issues.
- Invest in training – build internal capacity to sustain the system.
- Use technology – digital dashboards can simplify data collection and monitoring.
- Seek external verification support – pre-audit reviews reduce surprises in the certification audit.
Following these practices ensures smoother audits and stronger long-term ESG performance.
Future Trends
By 2027, Malaysia’s i-ESG roadmap signals a shift from voluntary ESG adoption toward stronger compliance expectations. Public listed companies and supply-chain-exposed firms are likely to face the earliest pressure. While SIRIM 55 ESG Certification is not yet mandatory, it is increasingly recognised as a practical pathway to demonstrate compliance and readiness.
Future trends include:
- Integration with IFRS S1/S2 for global investor reporting.
- Greater reliance on digital tools for ESG data collection and verification.
- Expansion of assurance expectations, with ESG reports needing independent verification (e.g., under SIRIM 56).
- Sector-specific ESG metrics driven by international buyers and investors.
Companies preparing now will avoid last-minute compliance pressure and build lasting competitive advantage.

How SuSciCo Helps You Survive
At SuSciCo, we understand that companies rarely struggle because of poor effort. They struggle because every buyer, auditor, and investor uses a different system to judge their ESG rating. Our role is to simplify this complexity and prepare you to respond with confidence.
We do not issue certifications or ratings—that responsibility lies with accredited auditors and rating agencies. What we do is ensure you are ready. Your evidence is structured, your gaps are closed, and your disclosures are aligned with the expectations of each system.
Here is how we support you:
- Unified evidence preparation → We help you build a core set of policies, procedures, and records that can be adapted across multiple ESG rating systems, including EcoVadis, SMETA, and BSCI.
- Audit readiness support → Through gap analyses, mock audits, and corrective action planning, we prepare you for third-party inspections such as SMETA, BSCI, or SA8000.
- EcoVadis score improvement → We guide you in strengthening documentation, aligning with EcoVadis methodology, and closing evidence gaps to improve your ESG rating over time.
- Disclosure alignment for investors → We connect your sustainability reporting with frameworks used by FTSE4Good, MSCI, and S&P Global. This ensures your ESG rating reflects your strengths in the eyes of investors and capital markets.
Don’t waste resources on trial and error. Partner with a team that has guided Malaysian SMEs through EcoVadis, supplier audits, and SIRIM preparation—and get ready for the ESG ratings that matter most to your business.
Getting ready for SIRIM 55 ESG Certification requires planning, systems, and credible governance. SuSciCo supports organisations with readiness assessments, system design, mock audits, and staff training.
Get a SIRIM 55 readiness assessment today and start your journey toward certification with confidence. Request a Quote.
SuSciCo helps in implementing Sustainability Practices
At SuSciCo, we help companies implement a Customer-Centric Sustainability approach by integrating ESG principles into their strategies. Our services include GHG management, sustainability reporting (GRI, IFRS, Bursa Malaysia), supply chain optimization, and ISO 14001 EMS development. We offer PCF and LCA assessments, sustainable procurement strategies, and waste management solutions to align products and operations with customer expectations. Through tailored ESG training and stakeholder engagement, we empower businesses to reduce environmental impacts, foster innovation, and build trust for sustainable growth.



